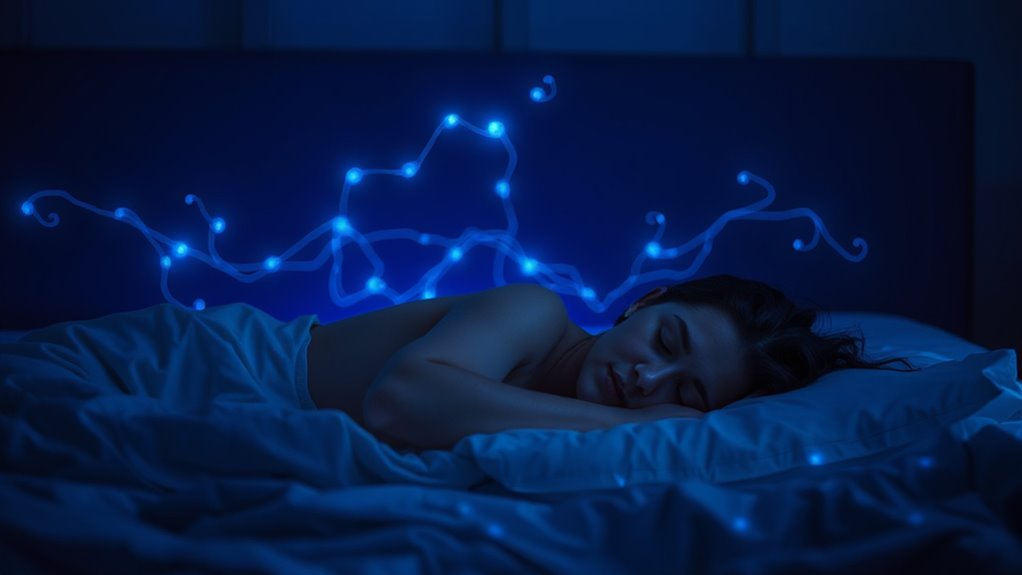
During REM sleep, your brain becomes highly active, working to organize, strengthen, and emotionally process recent experiences into lasting memories. Neural firing patterns resemble waking consciousness, especially in areas like the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, which help sort and interpret memories. This process also reduces emotional intensity, making you feel calmer upon waking. If you want to understand how this incredible memory work happens and affects your mental health, there’s more to discover.
Key Takeaways
- REM sleep activates the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex to organize and integrate recent experiences into long-term memories.
- Neural firing patterns during REM resemble waking activity, reinforcing connections related to recent memories.
- REM sleep facilitates emotional memory processing by reducing emotional intensity through targeted neural activation.
- The brain sorts and contextualizes memories, linking new experiences with existing knowledge for better retrieval.
- Overall, neural activation during REM sleep supports memory consolidation and emotional regulation, promoting mental well-being.
Have you ever wondered how your brain processes memories while you’re dreaming? During REM sleep, your brain becomes a hub of neural activation, firing up in ways that closely resemble waking consciousness. This heightened activity isn’t random; it plays a pivotal role in consolidating your memories. As neural pathways activate, your brain works to strengthen connections between neurons involved in recent experiences, helping to embed them into long-term storage. This process isn’t just about storing facts; it also involves integrating emotional components, which is essential for healthy emotional regulation. When your brain activates these neural circuits during REM, it helps you process emotional memories more effectively, reducing their intensity and making them less disruptive over time.
During REM sleep, specific areas of your brain light up, including the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, which are fundamental for memory consolidation. The hippocampus acts like a librarian, sorting through your recent experiences and deciding what’s worth saving. Meanwhile, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for higher-order thinking, is also active enough to help you make sense of these memories and their emotional context. This coordinated neural activation ensures that not only are your memories preserved, but they’re also integrated with existing knowledge, giving your experiences meaning. It’s like your brain is organizing files in a well-structured archive, making future retrieval easier and more meaningful. Additionally, data-driven strategies in understanding sleep mechanisms can enhance this natural process.
Importantly, this process supports emotional regulation by helping your brain reprocess emotionally charged memories. During REM sleep, your brain selectively weakens the emotional grip of traumatic or distressing memories. This is partly achieved through neural activation patterns that target emotional centers like the amygdala, reducing their response to certain memories. As a result, you wake up with a calmer emotional response to those experiences, which can improve your mental health over time. This neural mechanism underlying dream consolidation is why sleep, especially REM, is so essential for maintaining emotional stability and resilience.
In essence, your brain’s neural activation during REM sleep isn’t just about dreaming; it’s a sophisticated process that consolidates memories and helps regulate emotions. It’s why sleep feels restorative—not just physically, but mentally and emotionally. By actively processing memories and moderating emotional responses during dreams, your brain ensures you move through life with a better sense of balance and understanding. So, the next time you wake from a vivid dream, remember that your brain has been hard at work, strengthening your memories and fine-tuning your emotional well-being. Recognizing the importance of neural activation during sleep can motivate healthier sleep habits for overall mental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Dreams Influence Emotional Regulation?
Dreams influence your emotional regulation by helping you process feelings and experiences. Through dream symbolism, your mind interprets emotions, making sense of complex situations. This process supports emotional healing, allowing you to release stress and gain clarity. When you remember and reflect on your dreams, you can better understand your emotional responses, ultimately strengthening your resilience and helping you manage your feelings more effectively.
Can Dream Consolidation Improve Learning Skills?
Dream consolidation can definitely improve your learning skills. When you actively engage in lucid dreaming, you gain control over your dreams, which helps reinforce memories and problem-solving skills. Techniques like nightmare therapy also help reduce anxiety, freeing your mind for better learning. By practicing these methods, you strengthen your brain’s ability to process information, making it easier to retain new skills and knowledge in your waking life.
What Disorders Affect REM Sleep and Memory Processing?
Ever wonder why some sleep through the night and wake up foggy? Sleep disorders like insomnia, narcolepsy, and sleep apnea seriously affect REM sleep, disrupting your dreams and memory processing. These sleep disorders cause memory impairments, making it harder to learn and recall information. Ironically, in trying to rest, your brain struggles to consolidate memories, highlighting how essential quality REM sleep truly is for your mental sharpness.
How Does Age Impact Rem-Related Memory Consolidation?
As you age, you experience an age-related decline in REM sleep, which affects your ability to consolidate memories during this stage. Developmental differences mean that children have more REM sleep, aiding their memory processing, while older adults often have less, leading to potential memory issues. This decline impacts how effectively your brain processes and stores new information, highlighting the importance of healthy sleep habits throughout life.
Are There Ways to Enhance Dream Recall for Better Memory?
You might think enhancing dream recall isn’t worth the effort, but it can actually boost your memory. Try lucid dreaming techniques to become aware during your dreams, then keep a dream journal to record details immediately. This practice sharpens your recall and reinforces memory consolidation. Regularly engaging in lucid dreaming and journaling strengthens your ability to remember dreams, ultimately improving your overall memory and understanding of your subconscious mind.
Conclusion
As you experience REM sleep, your brain actively works to consolidate memories, turning fleeting thoughts into lasting ones. Imagine you’re studying for a big test; during REM, your brain sorts through information, strengthening important facts. Just like a student who dreams about the exam and wakes up feeling more prepared, your mind is quietly organizing your experiences. Embrace these nightly processes—they’re your brain’s way of helping you learn and grow while you sleep.